What Does Triple Rule Is Used to Describe a Codon
Translation is the process of converting the genetic information in the mRNA strand to the form of a protein. This demonstrated that three nucleotides specify each amino acid.
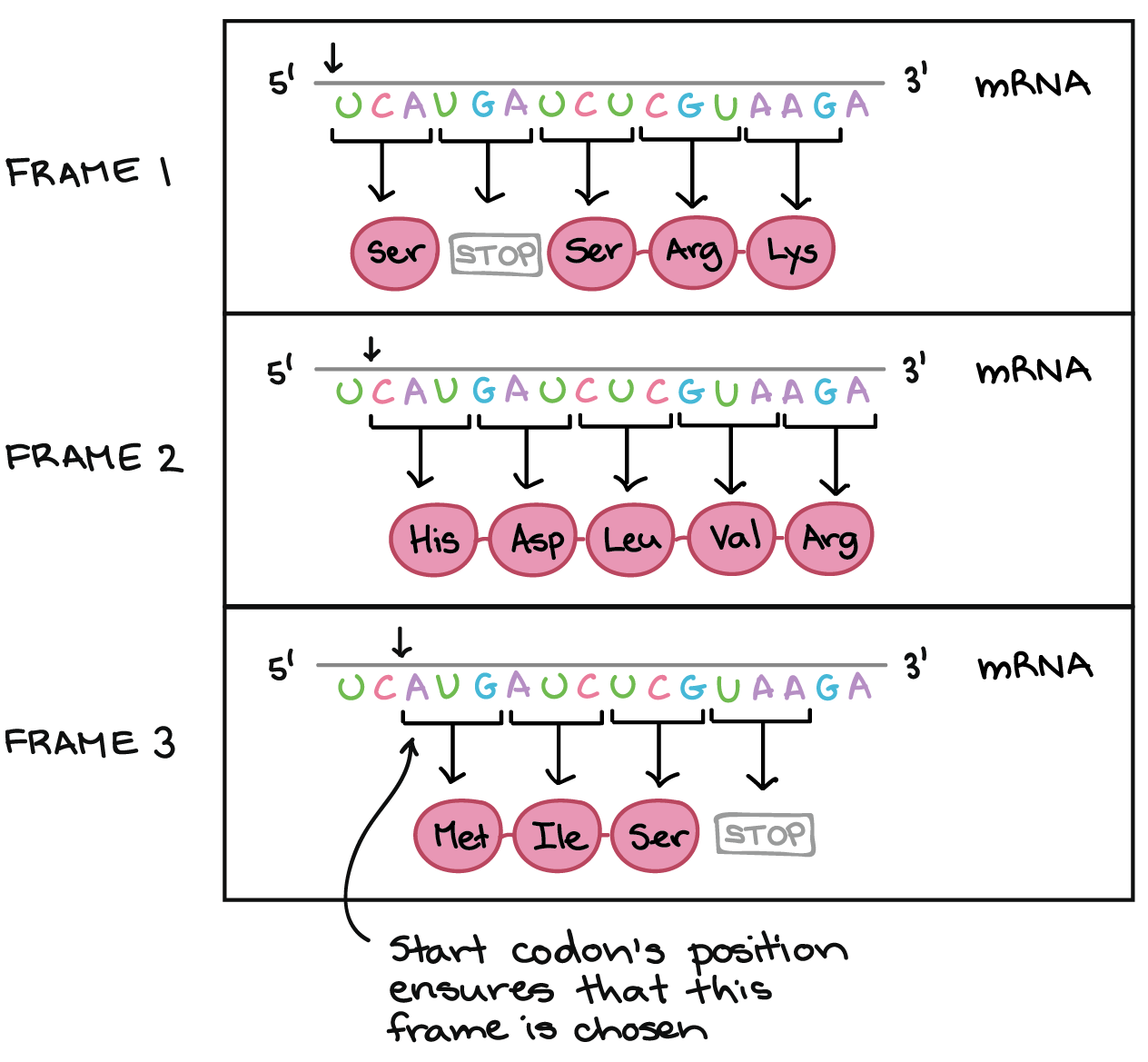
The Genetic Code Codon Table Article Khan Academy
Sets found in the same folder.
. There are 64 different codons. A sequence of three nucleotides which together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule. The genetic code includes 64.
If were talking about a set of three nucleotide bases on DNA we refer to them as a triplet. However as a triplet on mRNA codes specifically for an amino acid they are referred to as codons. How you determine your amino acids are by these steps.
The number of codon values is roughly triple the number or amino acids plus a stop codon allowing for redundancy. These nucleotide triplets are called codons. A sequence of three nucleotides which together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule.
Cells decode mRNAs by reading their nucleotides in groups of three called codons. Review of Codon Recognition. A codon is a coding language comprised of 3-letter words that genes use.
Codons are made up of any triplet combination of the four nitrogenous bases adenine A guanine G cytosine C or uracil U. Codons in an mRNA are read during translation. Called also triplet.
MRNA holding second tRNA moves to first position in ribosome. Second tRNA enters ribosomal site with 2nd amino acid. Up to 24 cash back After you have decoded all of your DNA bases into the RNA bases you are ready to use the codon chart.
After DNA is transcribed into RNA the RNA is translated into a polypeptide sequence. A specific sequence of three consecutive nucleotides that is part of the genetic code and that specifies a particular amino acid in a protein or starts or stops protein synthesis. When one or two nucleotides were inserted protein synthesis was completely abolished.
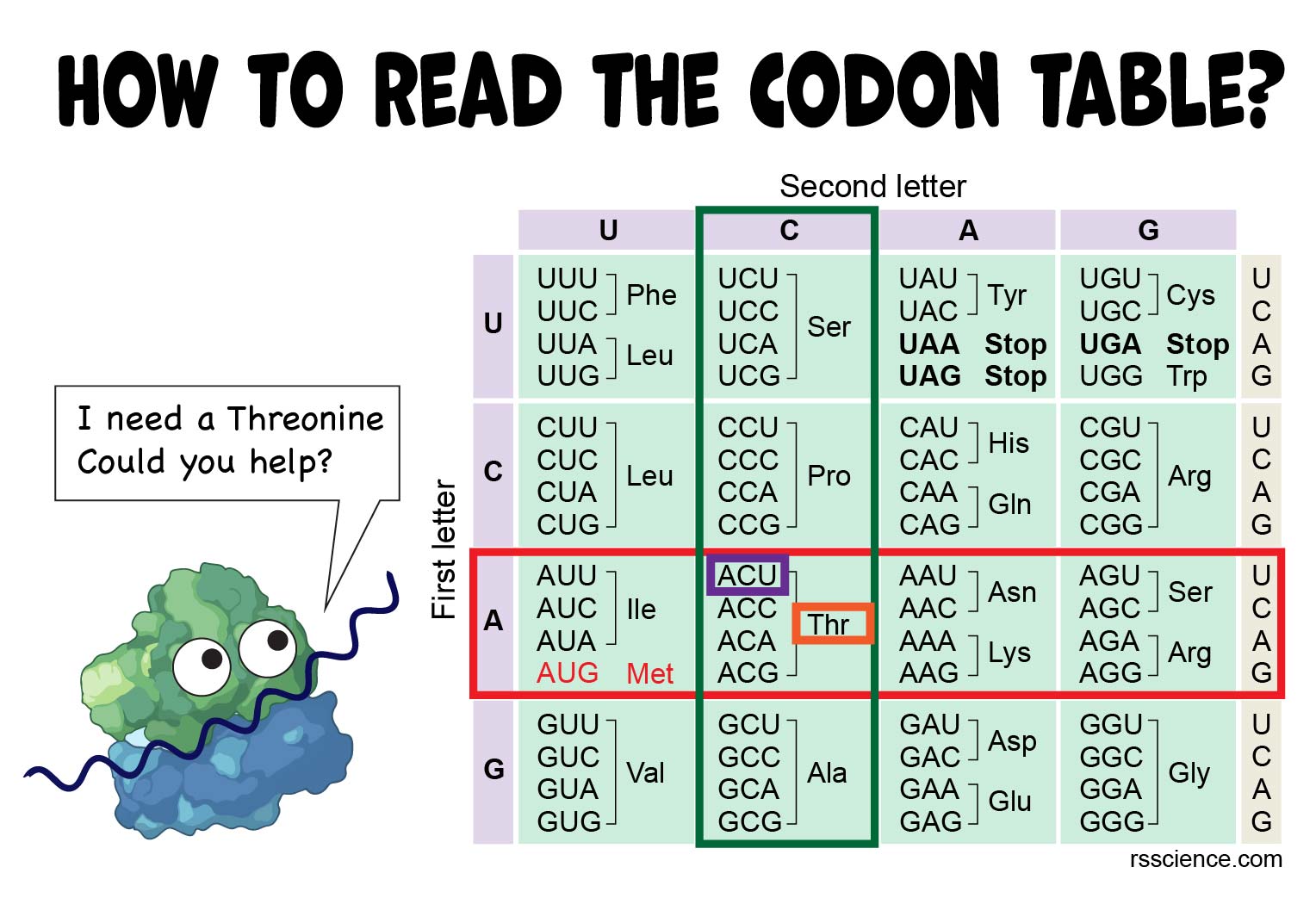
A codon is used with inference to an mRNA triplet. Use your new code in this case it is AUG to read the chart. Some amino acids are encoded by more than one.
That specific rule set is referred to as the genetic code. One codon AUG serves two related functions. Codon definition a triplet of adjacent nucleotides in the messenger RNA chain that codes for a specific amino acid in the synthesis of a protein molecule.
Codon and anticodon are nucleotide triplets which specify a particular amino acid in a polypeptide. The new end is the hot end where new residues are added red. MRNA molecules contain triplets of nucleotides known as codons each of which codes for an amino acid or a stop signal for translation.
Each codon corresponds to a single amino acid or stop signal and the full set of codons is called the genetic code. Codons are essentially triple nucleotide sequences that tRNAs which also enter ribosomes recognise and bind to with each tRNA introducing a peptide that corresponds to a specific codon sequence. These triplets are called codonsWith three exceptions each codon encodes for one of the 20 amino acids used in the synthesis of proteins.
Transfer RNA Transfer RNA are able to read codons. Each three nucleotides triplet in the genetic code known as a codon encodes a specific amino acid or stop signal. That produces some redundancy in the code.
A specific rule set exists for the storage of genetic information as a nucleotide sequence either on DNA or mRNA molecules in order to synthesise proteins. Codon in genetics any of 64 different sequences of three adjacent nucleotides in DNA that either encodes information for the production of a specific amino acid or serves as a stop signal to terminate translation protein synthesis. In particular find the smallest power of 4 21 which turns out to be 3.
TRNA is another name for Transfer RNA. 61 specify amino acids and 3 are used as stop signals. TRNA binds to initiation codon AUG 3.
DNA - RNA Codons. Here are some features of codons. The old end is the cold end blue.
Every three nucleotides in the RNA sequence is read as a separate codon which encodes a specific amino acid. One start codon AUG marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine. REMainder of ribosomes comes into place 4.
All strands are synthesized from the 5 ends to the 3 ends for both DNA and RNA. For example the codon UAC uracil adenine and cytosine specifies. Peptide bond between amino acids forms and first tRNA is released 2.
A codon is a DNA or RNA sequence of three nucleotides a trinucleotide that forms a unit of genomic information encoding a particular amino acid or signaling the termination of protein synthesis stop signals. TRNA molecules also contain triplets of nucleotides known as anticodons which are complementary to codons. It signals the start of translation.
When three nucleotides were inserted the protein was synthesized and functional. Protein chains are synthesized from the amino ends to the carboxy ends. When its time for the stop codon to be translated instead of a tRNA a protein called the release factor binds and causes the ribosome to release the produced peptide sequence.
Supporting all amino acids plus a stop codon requires at least 21 distinct codon values. Strands and Directions of Synthesis. This is why codons are known as the triplet code.
Three stop codons mark the end of a protein. If your DNA sequence is TAC then when you decode it it will translate into the RNA AUG. The code is read in triplet sets of nucleotide bases called codons that designate specific amino acids.
Most of the amino acids being encoded by more than one codon. The genetic code is a sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA and RNA that code for the production of specific amino acids. Most codons specify an amino acid.
Amino acids are linked together to form proteins.
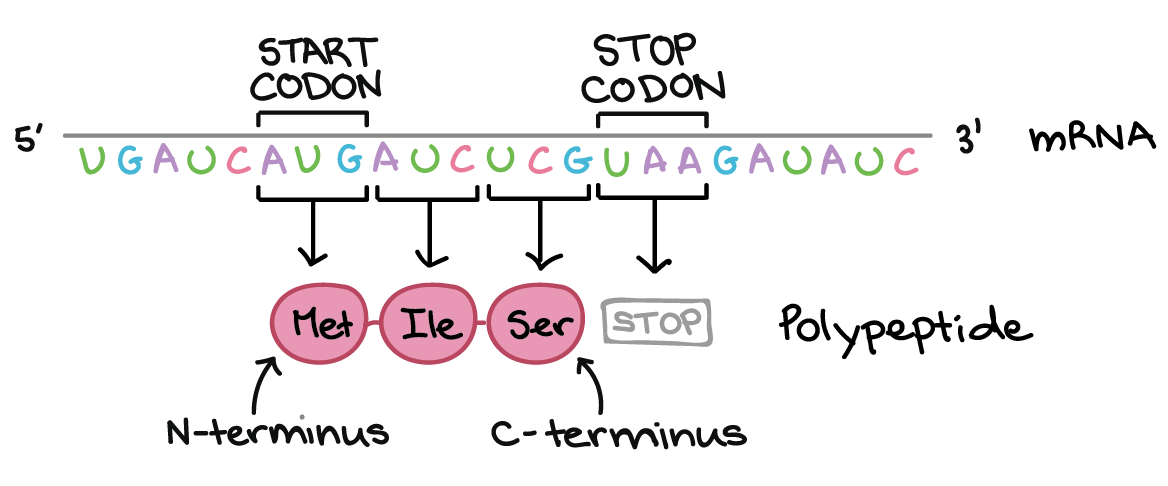
The Genetic Code Codon Table Article Khan Academy

How To Read The Amino Acids Codon Chart Genetic Code And Mrna Translation Rs Science
Why A Triplet Code Gene Expression Part 1 Reading Genes To Make Proteins Passel

No comments for "What Does Triple Rule Is Used to Describe a Codon"
Post a Comment